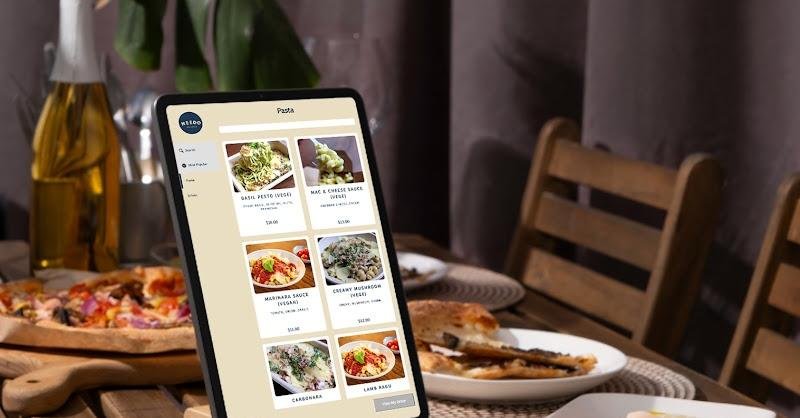
We are witnessing a revolution in meal ordering. The days of depending only on wait personnel to accept orders are over. Frequently deployed via touchscreen kiosks, self-ordering systems for restaurants quickly transform the eating experience.
But what drives these seemingly basic interfaces? This blog digs into the interesting working mechanism of technology that powers self ordering systems for restaurants.
The Growth of Self-Service Technology
The notion of self-service technology has been introduced previously. Vending machines, ATMs, and self-service checkout counters have existed for decades. However, the use of this technology in the restaurant business has grown significantly in recent years. Factors such as rising labour costs, the need for speedier service, and the growing preference for contactless transactions have pushed the growth of self-ordering systems.
The Core Components: Hardware and Software Working in Collaboration
- Hardware Essentials: The kiosk is the most visible aspect of the self-ordering system for restaurants. It comprises a touchscreen display for client contact, a computer unit that processes data and runs the programme, and a payment terminal for safe transactions. Additional hardware components may include receipt printers, barcode scanners for loyalty programmes, and help buttons.
- The Software Engine: The software is what makes the self-ordering method so effective. This programme often includes many critical components:
- Operating System: The operating system (OS) is the basic layer comparable to that runs on your computer. Android and Linux-based operating systems are popular alternatives for kiosk systems because of their reliability and security.
- (UI) User Interface and User Experience Design (UX): Customers engage directly with the user interface (UI). It should be intuitive, visually beautiful, and simple to use. A well-designed UI and a great user experience (UX) increase consumer happiness and encourage repeat kiosk use.
- OMS: The order management system (OMS) is the primary component of the self-ordering system. It accepts consumer orders, sends them to the kitchen, and monitors their status. The OMS integrates seamlessly with the restaurant’s existing point-of-sale (POS) system to streamline order processing and payment collection.
- CMS: The content management system (CMS) enables restaurant personnel to alter menus, prices, and promotional offers that appear on the self-ordering system. A user-friendly CMS allows staff to manage accurate and up-to-date information accessible to customers through the kiosks.
Real World Case Studies
- Taco Bell: Taco Bell’s self-ordering system, dubbed “Taco Bell Go Mobile,” combines kiosks, mobile app ordering, and drive-through improvements. The system provides a smooth and personalised ordering experience, including customisations, saved preferences, and loyalty benefits. After using this approach, Taco Bell has experienced a significant boost in digital orders and consumer involvement.
- BurgerFuel: BurgerFuel, a well-known New Zealand gourmet burger business, has successfully integrated self-service kiosks into its restaurants. Customers can use the kiosks to customise their burgers, choose from add-ons, and easily make payments. The use of innovative technology has not only improved the client experience but also simplified processes and boosted order accuracy. BurgerFuel claimed a substantial rise in average order value and customer satisfaction since implementing kiosks, showcasing the effectiveness of technology in elevating the dining experience.
Future of Self Ordering System for Restaurants: Integration with Emerging Technologies
The future of self-ordering systems is tied to their integration with latest technologies such as AI, the Internet of Things and machine learning. AI-powered systems may analyse client data to provide personalised suggestions, optimise menu options, and improve the eating experience. IoT integration may improve kitchen efficiency and provide real-time inventory control.
- Voice-activated ordering: Voice-activated ordering is an exciting advancement in self-ordering technology. Restaurants are investigating using voice assistants such as Amazon Alexa and Google Assistant to allow consumers to place orders via voice commands. This hands-free technique improves ease and accessibility, especially for consumers with impairments.
- Enhanced Mobile Integration: As mobile devices grow more common, self-ordering systems will continue to work smoothly with mobile apps. Customers may use their cell phones to place orders, make payments, and manage loyalty points. Enhanced mobile integration ensures a consistent and convenient user experience across different touchpoints.
- Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Solutions: The restaurant sector is focusing more on sustainability and environmentally friendly practices. Self-ordering systems can help with these efforts by lowering paper use through digital receipts and menus. Additionally, data acquired from self-ordering systems can assist restaurants in identifying areas for waste reduction and resource optimisation.
Conclusion:
Self ordering systems for restaurants have transformed the eating experience, providing greater convenience, personalisation, and efficiency to both consumers and operators. The technology behind these devices includes complex hardware and software aspects assisting in streamlining operations, minimising costs, and boosting revenue.
As the industry evolves, integrating new technology and novel features will improve the capabilities of self-ordering systems. By staying ahead of these changes, restaurants may guarantee that they satisfy evolving client expectations and maintain a competitive advantage in the market.
The future of self-ordering systems is bright, with limitless opportunities to enhance the eating experience and optimise restaurant operations. As more restaurants adopt this technology, it will indeed become essential to the modern eating experience.